Series Rated Vs Fully Rated: Understanding the Short Circuit Current Protection Systems

January 29, 2024

Series rated vs fully rated: this article provides an understanding of short circuit current protection systems. Circuit Breakers are designed to provide overcurrent protection for electrical networks and connected loads. Short Circuit Current protection is one such example of overcurrent protection and very often needs to be done in a coordinated way to ensure full protection at every level of the electrical network. In protection coordination schemes, electrical designers may design the system as fully rated or series rated systems in order to achieve short circuit current protection. Understanding the differences between these two systems can have a significant impact on electrical safety considerations.
What is a Series Rated Protection System?
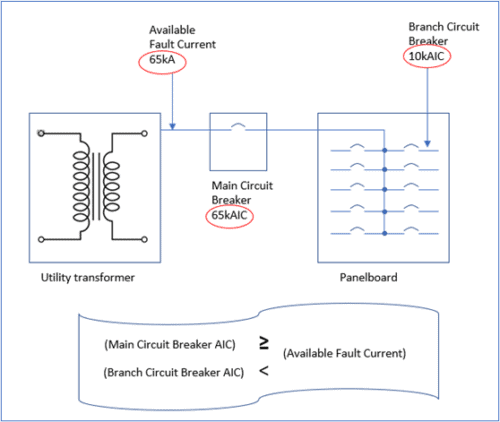
According to National Electric Code (NEC 110.22 and NEC 240.86), a series combination system is a system of circuit breakers connected in series such that a circuit breaker used on the network can have an interrupting rating lower than the available fault current, provided it is connected on the load side of an acceptable overcurrent protective device having an interrupting rating equal or higher than the available current on the line side of the device. Under the code manufacturers can publish a series combination listing only after they have tested these series combination of devices under fault conditions to ensure it can safely clear faults and protect the equipment.
Advantages of Series Rated Protection
By using a series rated protection system, you can save some bucks. Instead of upgrading the branch circuit breakers to costlier breakers that have higher interrupting capacities, series rated protection provides an alternative. This particularly has a significant cost advantage in installations with very high available fault current. However, this also means that the customer can only use a single brand of breakers for panel designs since there are no inter-manufacturers series-rated systems.
What is a Fully Rated Protection System?
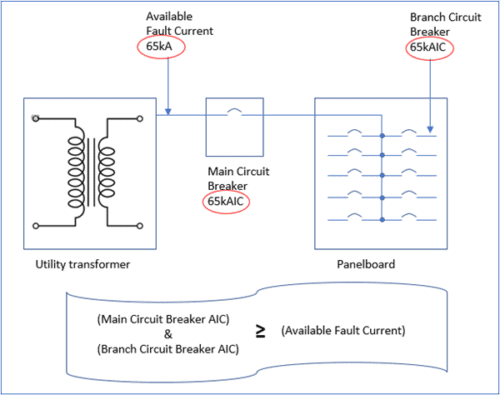
Now, let’s switch gears and explore fully rated protection systems. The fully rated system is a more direct or traditional way of handling short circuit current protections. In this system, every overcurrent device (main and branch circuits) is rated with interrupting capacities equal to or greater than the available fault current at the line side terminals of each device.
Advantages of Fully Rated Protection
- Enhanced Safety: With fully rated protection, you can rest easy knowing that your entire electrical system is equipped to handle the maximum fault current. By having both the main breaker and feeder breakers fully rated, the risk of equipment damage and electrical hazards is significantly reduced.
- Regulatory Compliance: In certain industries or jurisdictions, fully rated protection may be a requirement. It’s essential to stay informed about the specific regulations in your area and ensure your electrical system complies with the necessary codes.
Prevent Short Circuits with Noark Components
Whether you opt for series rated or fully rated protection, the key takeaway is the importance of electrical safety. While series rated protection can be a cost-effective solution, fully rated protection offers enhanced safety. Ultimately, the choice depends on your specific needs and circumstances.
More Information
Remember, when it comes to electrical protection, seeking professional advice is crucial. Contact Noark Electric to help determine the best circuit protection components for your unique requirements.
Related Story
Noark Electric Highlights Their Breaker Modification Center
Noark is well-known for their world-class manufacturing and rigorous testing of their products that meet or exceed the highest performance standards in the industry. What should be better known is their ability to rapidly modify or produce products that satisfy their customers’ unique specifications. In this article, Rob Farrell, Marketing Director of Noark Electric, and Robert McKean, Assembly Technician at the Noark Power Breaker Modification Center discuss the Mod Center and how it is expanding to better serve electrical OEMs across North America.





